Captive insurance, also known as self-insurance or microcaptive, has emerged as a powerful tool for businesses seeking greater control over their risk management strategies. Born out of the need for specialized coverage for unique or high-risk exposures, captive insurance offers a customizable solution that goes beyond traditional insurance offerings.
One key aspect that sets captive insurance apart is the IRS 831(b) tax code, which allows small insurance companies to be taxed on their net investment income only. This favorable tax treatment allows businesses to accumulate funds within their captive insurance company, creating a potential source of tax-efficient funds for future claims or investment opportunities.
By establishing a captive insurance company, businesses essentially take on the role of an insurer, providing coverage for their own risks. This allows them to tailor policies specifically to their needs, ensuring adequate protection while avoiding potential gaps in coverage often associated with off-the-shelf insurance products.
Additionally, captive insurance enables businesses to better manage their risk profiles by gaining a deeper understanding of their unique exposures. Through rigorous risk analysis and ongoing risk assessment, companies can implement proactive strategies to mitigate risks and strengthen their overall risk management framework.
Breaking free from traditional insurance structures and embracing the power of captive insurance empowers businesses to not only optimize their risk management strategies but also potentially realize significant financial benefits. By taking control of their insurance programs, businesses can better protect their assets, enhance their financial stability, and make informed decisions that align with their long-term business goals.
The world of captive insurance is ripe with possibilities, and as businesses seek to gain a competitive edge, unlocking the potential of captive insurance could prove to be a game-changer. In the following sections, we will delve deeper into the intricacies of captive insurance, exploring its benefits, considerations, and how it can be leveraged to revolutionize risk management practices.
Understanding Captive Insurance
831b
Captive insurance is a unique and powerful tool that offers businesses the opportunity to take control of their insurance needs. Unlike traditional insurance, which involves purchasing coverage from third-party insurers, captive insurance involves forming an insurance company that is owned and controlled by the insured business itself.
By establishing their own captive insurance company, businesses can gain greater flexibility and customization in their insurance coverage. This enables them to tailor policies specifically to their unique risks and needs, providing a level of coverage that is often more comprehensive and cost-effective than what is available in the commercial market.
One popular type of captive insurance is known as the 831(b) captive, named after the section of the IRS tax code that governs its operation. These captives are typically designed for small and mid-sized businesses and offer certain tax advantages, such as the ability to recognize premiums as tax-deductible expenses.
It’s important to note that captive insurance has attracted some attention from the IRS, specifically concerning the abuse of these tax advantages through microcaptives. Microcaptives are captives with premiums that fall under a specific threshold. While legit uses of captive insurance can bring substantial benefits, it’s crucial for businesses to adhere to the IRS guidelines to avoid any potential tax scrutiny.
In summary, captive insurance provides businesses with an alternative to traditional coverage, allowing them to have greater control over their insurance programs. The 831(b) captives, in particular, offer tax advantages to eligible businesses. However, it is essential for businesses exploring captive insurance to ensure compliance with IRS regulations to maximize the benefits and minimize any possible scrutiny.
The Benefits of the 831(b) Tax Code
When it comes to captive insurance, the 831(b) tax code offers some significant advantages. One of the key benefits is the ability for small and mid-sized businesses to form their own insurance company and enjoy certain tax advantages. With this provision, eligible companies can make an 831(b) election and enjoy a reduced tax rate on their insurance income.
The primary advantage of the 831(b) tax code is the ability to retain a larger portion of underwriting profits within the captive insurance company. Under normal circumstances, these profits would be subject to higher tax rates. By electing the 831(b) tax code, businesses can keep more of their insurance earnings, which can be reinvested in the company or used for other strategic purposes.
Moreover, forming a captive insurance company under the 831(b) tax code can provide businesses with greater control over their insurance coverage and claims management. Unlike traditional insurance policies, captives allow companies to tailor coverage to their specific needs, mitigating risks more effectively. Additionally, businesses can directly benefit from any cost savings that arise from favorable loss experience.
In summary, the 831(b) tax code provides enticing opportunities for small and mid-sized businesses to leverage captive insurance as a strategic financial tool. By taking advantage of this provision, companies can retain more underwriting profits, exercise greater control over their insurance coverage, and potentially achieve cost savings. Understanding the benefits and implications of the 831(b) tax code is crucial for any business exploring the world of captive insurance.
Limitations and Considerations for Microcaptive Insurance
When considering the implementation of microcaptive insurance, it is crucial to acknowledge certain limitations and take them into consideration. These factors can impact the effectiveness and success of utilizing this insurance strategy.
First and foremost, it is important to note that microcaptive insurance is subject to strict regulations outlined under the IRS 831(b) tax code. This specific tax provision sets certain requirements in terms of the annual premium and net premium income for microcaptive insurers. Being compliant with these regulations is essential to ensure the benefits of the captive insurance arrangement.
Another limitation to keep in mind is the potential complexity and administrative burden that comes with establishing and maintaining a microcaptive insurance company. This type of insurance is often best suited for medium to large businesses that have the resources and expertise to handle the associated responsibilities. It may not be a suitable option for smaller organizations that lack the necessary capabilities and infrastructure.
Additionally, it is important to consider the potential risks involved in microcaptive insurance. Like any insurance arrangement, there is always a degree of uncertainty and potential for financial loss. Conducting a thorough risk assessment and understanding the potential exposures is vital to ensure that the microcaptive arrangement adequately addresses the specific risks faced by the insured party.
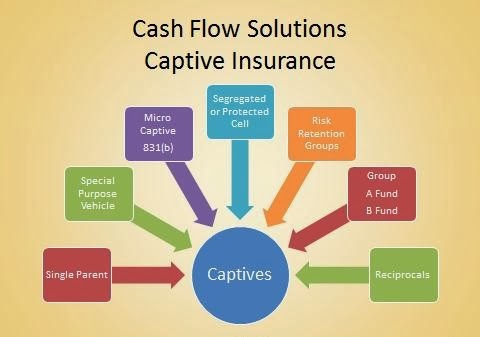
In conclusion, while microcaptive insurance can offer unique advantages such as cost savings and increased control over insurance programs, it is essential to approach it with caution and awareness of its limitations. By staying compliant with relevant regulations, having the necessary resources, and conducting proper risk assessment, businesses can unleash the power of captive insurance effectively.
