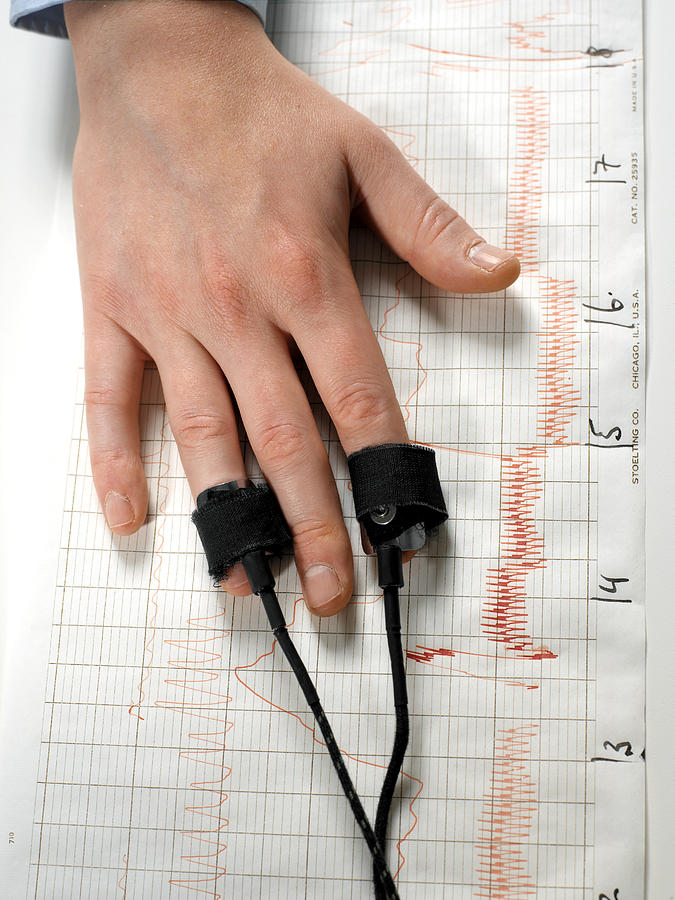
Welcome to the fascinating realm of lie detector tests, where truth-seeking mechanisms intersect with the intricacies of human behavior. These tests, often conducted in high-stakes scenarios, hold the potential to unravel deception and expose hidden realities that evade the naked eye. While the idea of a lie detector test might evoke thoughts of suspenseful interrogations and tense courtroom dramas, the actual intricacies behind these tests are as intriguing as they are complex. Developed as a tool to aid in determining the veracity of statements, lie detector tests tap into a blend of physiological responses to uncover the authenticity of one’s words. So, let us delve into this enigmatic world, where science meets psychology in the quest for uncovering the truth.
Polygraph
History of Lie Detector Tests
Lie detector tests, also known as polygraphs, have a long and fascinating history. The concept of using physiological responses to detect deception dates back to ancient times, when individuals believed that physical reactions could reveal dishonesty.
In the early 20th century, the modern lie detector test began to take shape with the work of psychologist William Moulton Marston. Marston’s research focused on blood pressure and deception, laying the groundwork for the polygraph as we know it today.
The use of lie detector tests gained popularity in the mid-20th century, particularly in law enforcement and government settings. Despite ongoing debate about their accuracy and reliability, lie detector tests remain a widely used tool in various fields to uncover the truth.
Accuracy and Controversies
When it comes to the accuracy of lie detector tests, opinions are divided. Proponents argue that polygraph exams can accurately detect deception by measuring various physiological responses, such as heart rate, blood pressure, and respiration. However, critics point out that factors like anxiety, stress, and individual differences in physiological responses can lead to false results.
One of the main controversies surrounding lie detector tests is their admissibility in court. While some jurisdictions accept polygraph results as evidence, many courts view them skeptically due to concerns about reliability and the potential for manipulation. This has led to ongoing debates about the validity of using lie detector tests in legal proceedings and the impact they can have on the outcome of a case.
Despite the controversies surrounding their accuracy and reliability, lie detector tests continue to be used in various settings, including law enforcement, government agencies, and the private sector. While some believe they provide valuable insights into truthfulness, others argue that the inherent flaws of polygraph exams make them too unreliable to be considered a definitive measure of honesty.
Ethical Implications
When delving into the realm of lie detector tests, ethical considerations come to the forefront. One key concern revolves around the potential invasion of privacy. Subjects may feel uncomfortable or violated when asked personal questions under the scrutiny of a lie detector, leading to ethical dilemmas regarding consent and confidentiality.
Another ethical consideration is the reliability of lie detector tests. While they are commonly used in various settings, there is ongoing debate about their accuracy and potential for error. In situations where the stakes are high, such as criminal investigations, the reliance on polygraphs as the sole determinant of truth raises ethical concerns about the possibility of incorrect conclusions and unjust outcomes.
Moreover, the use of lie detectors can impact trust and relationships. Employers or authorities using polygraphs may inadvertently create an atmosphere of suspicion and distrust among individuals, ultimately influencing the dynamics of personal and professional interactions. This ethical dilemma raises questions about the broader societal implications of relying on lie detector tests as tools for determining truth and enforcing accountability.
